"The secret of change is to focus all your energy, not on fighting the old, but on building the new."
SOCRATES
Consultancy
Alephn Consulting advises companies in the health sector in the planning, assembly and execution of health information technology projects, in areas such as Interoperability, Diagnostic Imaging, Medical History and Information Flows, among others.
Radiology Projects
Determine the economic and financial viability and structure the project for the implementation of a RIS/PACS system inside a hospital or a radiological center,
taking into account the following steps:
- Analysis of proposals.
- Definition of supplier qualification.
- Choice of the manufacturer.
- Definition and validation of the project schedule.
- Definition of the infrastructure necessary for the deployment of the platform (Dicom Routers and Networks).
- Collection and construction of the information necessary for the parameterization of the system (Macros).
- Verification of the modalities and compliance with the DICOM standard or use of VNA failing that.
- Parameterization and verification of MWL channels for connection of modes and image flow.
- Definition of the scope of RIS/HIS integration.
- Definition of the scope of image migration and its schedule.
- Assembly and verification of the integration.
- Verification of compliance with the training schedule.
- Program of testing and analysis of traffic in the channels.
- White march.
- Deployment to production.
Home
Health Processes
Process management in a health institution, whether a hospital, clinic, diagnostic aid centers or another institution, is intended to provide tools for efficient decision-making. In addition, it is oriented towards the final satisfaction of customers while generating competitive and profitable advantages.
Process management, also known as BPM (Business Process Management), emerged in the commercial business world and has been applied to many fields; among them, the health sector.
In conclusion, the ultimate goal of process management is the continuous improvement and excellence of each procedure within a health facility. Only through management is it possible to control every resource, strategy and objective that you want to achieve in the short and long term.
Home
Electronic Medical Record
The Electronic Medical Record (EHR), also called electronic health history, is the global and structured set of information related to a patient's healthcare processes, supported by a computer platform.
The system allows the storage and retrieval of healthcare information based on digital procedures, designed to facilitate the monitoring of actions, annotations and instructions on actions in the health of citizens.
The EHR is the persistent, potentially multi-institutional longitudinal record of health, and the provision of care relating to a patient, to inform their health care and to provide a legal medical record of the care provided.
Alephn Consulting provides the methodology for the selection and implementation of this important information system.
Home
Interoperability
Interoperability is the ability of different information technology systems, software applications and networks to communicate and exchange data accurately, effectively and consistently, and to use the information that has been exchanged.
In the health ecosystem, interoperability allows health information systems to transcend the boundaries of the organization and promote the provision of effective health services, by providing the correct information to health care providers to understand and
address the issue of the health of individuals and populations. Systems, such as electronic health records, play a vital role because they facilitate a comprehensive and safe collection of interactions between people and the health care system.
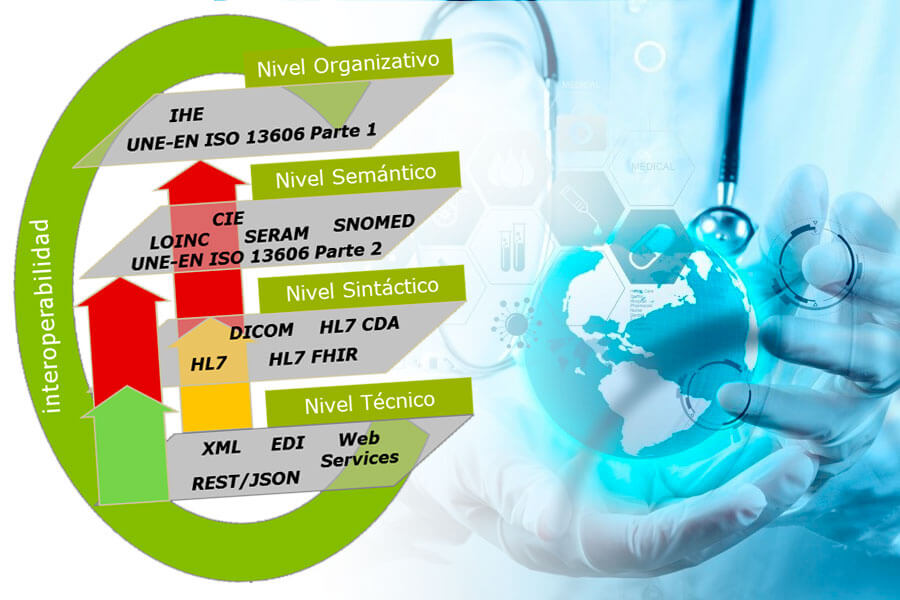
Alephn Consulting advises you on the determination of the channels and information that should be shared between different information systems..
Home
CES Teaching
TIC Fundamentals
The objective of this module is to transmit basic knowledge of information technology, on which today's world is based, to know the origin of the "digital" expression of these concepts and to determine their impact on the health sector.
The module is divided into three Units. In the first one, it begins with the exploration of the binary, decimal and hexadecimal numerical systems, explores the reason for the adoption of the binary system as the basis of computing and its implementation in digital circuits,
a journey is made from those of the first generation computers with vacuum tubes, to current technologies such as database engines, containers, artificial intelligence and their impact on future society. In the second unit we will address computer programming with the main
statements or pseudocode instructions applied in the Pseint simulator, the flowcharts and their interpretation, and we will perform several exercises to develop the necessary sequential thinking in addressing computer problems. Finally, in the final unit, we will enter
the world of relational databases, we will pose real-world problems, interpreted through entity-relationship diagrams, we will see the transformation of these diagrams into relational models and finally we will schedule queries to the database using the main SQL statements (Structured Query Language).
VIDEO CONFERENCE 1
VIDEO CONFERENCE 2
VIDEO CONFERENCE 3
SCRIPT PRIME NUMBERS
SCRIPT PYRAMID
Home
Health Process Modeling
The overall objective of this module is to make students aware of what interoperability is, what its value is, at what levels it can be implemented, what standards it must meet and what is its contribution to efficiency and safety in health. As a general definition,
we can say that interoperability is the ability of information systems to share data and enable the exchange of information between them. In the field of health, institutions aim to adopt information systems that allow efficient and patient-centered management, to achieve this efficiency
one of the objectives is interoperability; interoperability that allows transversal and longitudinal communication throughout all the structures of health services, guaranteeing the confidentiality and integrity of shared information. The module is divided into 4 units. In the first unit
we will learn about the different levels at which interoperability can be addressed, which are controlled vocabularies and what their impact is on clinical records in addition to terminology standards and specific models of representation. In the second unit, the reference medical terminology SNOMED-CT
will be reviewed, we will take a look at the structuring of the information through UML and we will finish with HL7 messaging in version 2.x. In unit three, the clinical document or CDA architecture and the DICOM diagnostic imaging standard will be reviewed; and, in the fourth and final unit,
we will study some electronic clinical registry models and the functions of the IHE health standards organization.
Sample Task For Activity 1
Sample Task for Activity 2
Diagram for Activity 2
Sample Task for Activity 3
Diagram for Activity 3
Sample Task for Activity 4
Diagram for Activity 4
Synchronous Communication of HL7 Messages
Home
Interoperability - Biomedical Engineering
In the health sector, interoperability is the ability of different information systems and software applications to communicate, exchange data and use the information exchanged. Interoperability
increases patient safety by allowing access and availability to clinical data.
Accessing clinical data in real time allows patients to be cared for from anywhere, improving quality and continuity of care. For this reason, it is imperative that the different health systems be able to exchange
information and transfer it from one system to another through specific interfaces, adapted or personalized, that structure the information in a similar way. In addition, today the exchange and portability of data
can be guaranteed technologically to achieve connected health systems.
The Interoperability module for Biomedical Engineering is divided into 6 units plus a Hackathon
- Unit 1 : Introduction to Programming and Principles of Interoperability
- Unit 2 : Controlled Vocabularies, Snomed-CT, JSON, UML and XML
- Unit 3 : Messaging HL7 Version 2.X
- Unit 4 : CDA - HL7 FHIR
- Unit 5 : DICOM - Open EHR
- Unit 6 : IHE - Archetypes
- HACKATHON
Class Documents
- Basic Programming and Fundamentals of Interoperability - Unit 1
- Example of Interoperability Diagram for Task
Home
Fundamentals of Technology - Computer Law
Computer Law includes the multiple iterations between ICT and Law, from which specific aspects arise such as the contracting of digitalizable intangibles, the intellectual property over them, electronic commerce,
the protection of personal data, the legal treatment of computer incidents, the technological aspects that impact labor relations and the provision of services.
The Fundamentals of Technology - Computer Law module is divided into 5 units plus a Hackathon
- Unit 1 : Basic ICT Fundamentals
- Unit 2 : Introduction to Databases-Virtualization-Containers- Artificial Intelligence
- Unit 3 : Basic Concepts of Artificial Intelligence
- Unit 4 : Basic Concepts of Quantum Computing
- Unit 5 : Evolution of ICT - Health Case
- HACKATHON
Class Documents
Home
Contact
Pedro Ortiz Tamayo
Systems and Computer Engineer UdeA
Database and Programming Specialist UNAL
Master's Degree in Health Information and Communication Technology UCES
Master in Innovation and Entrepreneurship U. Salamanca
Linkedin : 
Powered by Alephn
Home
 Alephn Consulting
Alephn Consulting